Table of Contents
- Background
- Paper
- Authors
- Related Publications
- Installation
- User Mode
- Developer Mode
- Usage Guide
- Main GUI
- Image Manipulation
- Neuron Segmentation
- Working with NWB files
- Loading NWB files
- Loading Activity
- Loading Videos
- Saving NWB files
- Technical Details
- Further Reading
- Manuals
- References
- Images & Datasets
- Licensing
Background
Paper
Comprehensively resolving neuronal identities in whole-brain images is a major challenge. We achieve this in C. elegans by engineering a multicolor transgene called NeuroPAL (a neuronal polychromatic atlas of landmarks). NeuroPAL worms share a stereotypical multicolor fluorescence map for the entire hermaphrodite nervous system that resolves all neuronal identities. Neurons labeled with NeuroPAL do not exhibit fluorescence in the green, cyan, or yellow emission channels, allowing the transgene to be used with numerous reporters of gene expression or neuronal dynamics. We showcase three applications that leverage NeuroPAL for nervous-system-wide neuronal identification. First, we determine the brainwide expression patterns of all metabotropic receptors for acetylcholine, GABA, and glutamate, completing a map of this communication network. Second, we uncover changes in cell fate caused by transcription factor mutations. Third, we record brainwide activity in response to attractive and repulsive chemosensory cues, characterizing multimodal coding for these stimuli.
For further details regarding the experimental set up and the methodology involved, please read the full paper.
@article{PMID:33378642, Title= {NeuroPAL: A Multicolor Atlas for Whole-Brain Neuronal Identification in C. elegans}, Author= {Yemini, Eviatar and Lin, Albert and Nejatbakhsh, Amin and Varol, Erdem and Sun, Ruoxi and Mena, Gonzalo E and Samuel, Aravinthan D T and Paninski, Liam and Venkatachalam, Vivek and Hobert, Oliver}, DOI= {10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.012}, Number= {1}, Volume= {184}, Month= {January}, Year= {2021}, Journal= {Cell}, ISSN= {0092-8674}, Pages= {272—288.e11}, URL= {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.012}}
Authors
This program is the result of the combined efforts of the following people:
- Eviatar Yemini
- Amin Nejabakhsh
- Erdem Varol
- Kevin Rusch
- Gonzalo Mena
- Matt Creamer
- Albert Lin
- Ruoxi Sun
- Aravinthan D. T. Samuel
- Liam Paninski
- Oliver Hobert
Venkatachalam Lab:
- James Yu
- Vivek Venkatachalam
- Maedeh Seyedolmohadesin
Kimura Lab:
- Chentao Wen
- Koutarou D Kimura
Please review our contributors page for more information.
Related Publications
- NeuroPAL: A Multicolor Atlas for Whole-Brain Neuronal Identification in C. elegans
- 3DeeCellTracker, a deep learning-based pipeline for segmenting and tracking cells in 3D time lapse images eLife
- Versatile Multiple Object Tracking in Sparse 2D/3D Videos Via Diffeomorphic Image Registration
Installation
For the latest compiled release that can be run independently of MATLAB, please check here, but please note that these may be outdated. To utilize the latest version live on Github, please follow these instructions:
User Mode
- Download the latest release.
- Extract the contents of the downloaded .zip to a location of your choosing.
Developer Mode
(Requires Python 3.9+ and MATLAB 2020b+.)
- Install the following dependencies: a. Mlapptools b. Bioformats Toolbox c. Image Processing Toolbox d. Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox f. requirements.txt or requirements-macos.txt
- Open Git Bash to your preferred working directory.
- Use
git clone https://github.com/Yemini-Lab/NeuroPAL_ID.git - Open
visualize_light.mlappin MATLAB’s AppDesigner.
Usage Guide
Main GUI
The main NeuroPAL GUI is the window that will appear when you open visualize_light.mlapp or run our compiled executable file. Though complex, we’ve written up a quick guide to help you find your way around below:

| Label | Description |
|---|---|
| x | Z-stacks of the NeuroPAL image and neuron labels. Green dots indicate named neurons, red dots unnamed ones. |
| y | The maximum intensity projection of the entire image. |
| z | This slider allows you to move through different z-stacks. |
| a | This is NeuroPAL’s main menu. From left to right, it contains the File menu, the pre-processing menu (where you can downsample or adjust the threshold), the Image menu (where you can manipulate the image and adjust its gamma or histogram), the Neurons menu (where you can import neurons and perform batch actions), the Display menu (where you can adjust what information NeuroPAL displays), the Analysis menu (where you can save your work), and a Help menu with convenient links. |
| b | This is the metadata menu. From left to right, you can open a NeuroPAL image, save your work, and view and edit metadata related to the worm you’re currently viewing, such as the body part on display, the worm’s age, its sex, its strain, and any additional notes. |
| c | This is the ID menu. From left to right, you can begin auto-IDing, you can define the details of your manual ID, and you can change what happens if you click anywhere on x. |
| d | Here you can select the color channels NeuroPAL_ID uses to visualize its images. |
| e | If you’re using our (as yet WIP) auto-identification function, this space is where you can designate the specific method you’d like the program to use. You’ll also see a list of neurons the program believes to be nearby as well as an indication of how confident it is in its ID. |
| f | This is where you can easily navigate various ganglia and browse lists of neurons you’ve identified as well as neurons that should exist in the selected region but that have yet to be ID’d. |
Image Manipulation
The Image sub-menu in NeuroPAL’s main menu (“a” in the main GUI) contains a number of options. If you select “Adjust Histogram”, a separate window will pop up in which you can adjust the luminosity of individual channels with the guidance of a histogram. Below is a quick guide to that window.

| Label | Description |
|---|---|
| x | Maximum intensity projection of your NeuroPAL image. |
| y | A (Pixel Number x Pixel Intensity) histogram of all visible channels. |
| z | A tab group displaying the individual channel gammas and their curves. |
| a | This is a list of all currently supported channels. Checking a channel will render it both in the image and in all plots. |
| b | This is the min/max menu. Here you can define the minimum and maximum intensities represented in any given channel. |
| c | Clicking on a given channel’s lock toggle will prevent it from being edited. |
| d | Clicking on a given channel’s reset button will restore it to what it was before the histogram window was opened. |
| e | This is the settings menu. Here you can adjust the gamma across all channels, save your histogram in a guide file, and load and display saved guide files. |
Neuron Segmentation
The Neurons sub-menu in NeuroPAL’s main menu (“a” in the main GUI) contains a number of options. If you select “Auto Segmentation”, a separate window will pop up allowing you to segment the image and obtain a list of automatically detected neuron centers. Below is a quick guide to that window.

| Label | Description |
|---|---|
| x | By default, a maximum intensity projection of your NeuroPAL image. Can also be set to display a particular z-slice. |
| y | A slider allowing you to browse specific z-slices. |
| a | This panel features 3 sub-menus: “Neuron”, which displays information on neurons post-segmentation (unpopulated by default) and allows users to either export neuron centers or pass them back into the main NeuroPAL_ID window, “Image”, which allows you to select a specific range of slices to segment or to switch back to the maximum projection, and “Credit”, which features information regarding the origins of the particular segmentation module being used. |
| b | This panel features the core controls of the auto-segmentation window. The black out tool allows you to zero out specific sections of the image (such as the gut) to minimize false positives. The histogram tool will open the histogram window described earlier. The “Generate” button starts the segmentation process and the “Reset” button undoes all changes made to the image since the window was opened. |
| c | This panel allows users to edit the parameters of the segmentation process. Hovering over each label will show information regarding what each parameter means. |
| d | These panels allow users to change some of the segmentation settings. By default, the noise filter level is calculated automatically using the 95th percentile of pixels, but it can also be set manually. The cell filter specifies the measure by which all detected segments are filtered – either by the minimum size (in microns) or by the neuron count (in which case only the n biggest segments are kept). |
Working with NWB Files
NeuroPAL_ID natively supports loading, viewing, editing, and saving data in the NWB format using the ndx-multichannel-volume extension. Future software expansions will build on this support as well.
Click on each of the previews below to view them in full resolution.
Loading Activity

Loading Video

Saving NWB Files

Technical Details
Class, Package, and Usecase Diagrams
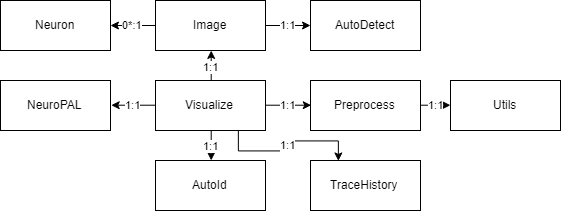
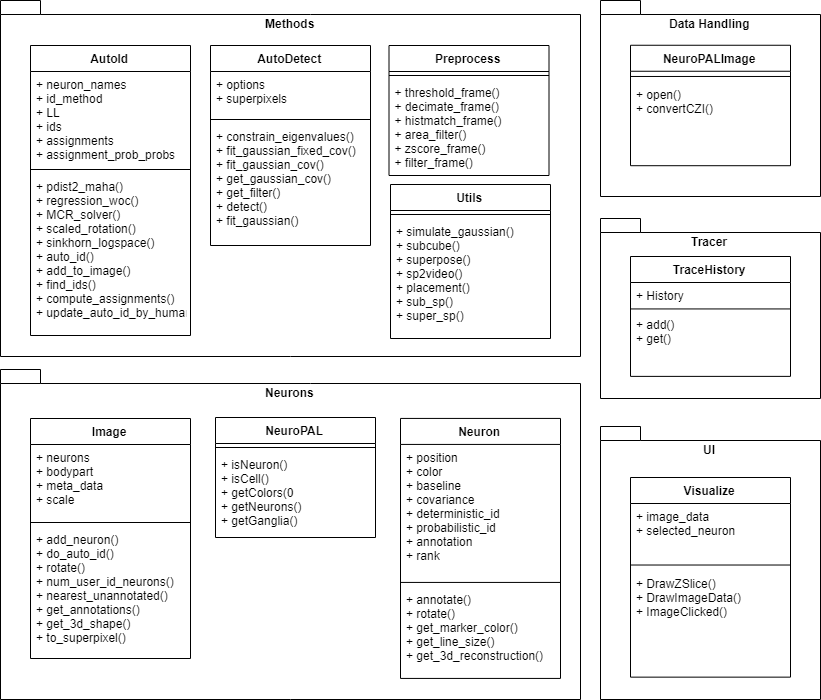
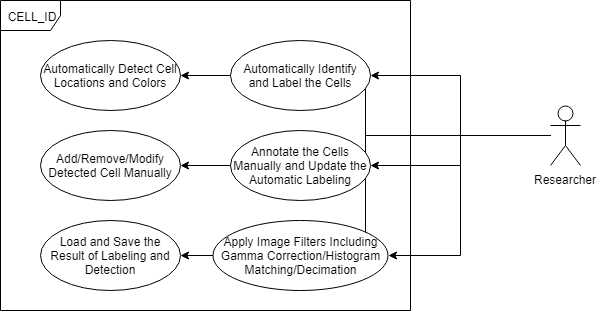
To build a fast and scalable system we followed object oriented design practices. We identified internally coherent and externally independent classes in our environment and established their properties and behavior, as well as their interactions with other modules. We have separate packages for data handling, methods, logging, biological objects, and user interface. Each of these packages contains relevant classes and the functionalities of the system is built upon the interactions between the classes. For reusability purposes we tried to develop a modular system with independent modules. This allows the users of the system to reuse different compartments of the system for other purposes.
Further Reading
NeuroPAL_ID is a complex piece of software that can be daunting at first but proves worthwhile if you put in the time to learn how to use it. There are several manuals that explore both NeuroPAL and the IDing process at various depths, and we strongly recommend that new users read these to get a sense of how to get the most out of NeuroPAL. If you’re new and making use of our introductory manuals, you may also want to practice with the specific image volumes they feature.
Manuals
- README 1st: A Quick Start Guide
- NeuroPAL Software Manual
- Using NeuroPAL for ID
- Configuring Your Microscope for NeuroPAL
References
- NeuroPAL Reference Manual
- OH15500 ID Reference Manual
- NeuroPAL Settings for Zeiss LSM Microscopes
- NeuroPAL Reporters + Neuron Colors
- Reporters + Expression tested for NeuroPAL
- Metabotropic Receptor Reporters
- NeuroPAL Reporter-Fluorophore Landmarks
- Panneuronal GCaMP6s + TagRFP-T Reporters
Images & Datasets
- NeuroPAL Zenodo Community
- Image Volumes Shown in the ID Manuals (To Practice ID’ing)
- 10 Young-Adult otIs669 (OH15262) Animals
- 3D NeuroPAL Atlas (NeuroML - Open Source Brain)
- OH16230 (21 heads & 21 tails) + OH15500 (7 heads) Data
You can also take a look at some of the published work done using NeuroPAL here.
Licensing
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.